04: Progress Monitoring
Presentation
Progress monitoring is the process of collecting and analyzing data over time to measure student performance and evaluate the effectiveness of instruction. Based on the student’s present level of performance (or baseline) and the goal, a data collection method is selected and expected rate of progress over short intervals of time are determined. Data is collected using the selected performance measure on a routine basis, such as daily, weekly or monthly. Progress toward meeting student goals is measured by comparing expected and actual rates of learning. Based on these measurements, teaching is adjusted as needed. In this module, you will learn the steps of effective progress monitoring to accelerate student progress.
Review the following video to learn more:
While you are viewing this module, think about:
- What are key components of effective progress monitoring?
- How can progress monitoring improve results for students with disabilities?
In the following poll:
- Rate your level of comfort with progress monitoring on a scale of 1-5 (1 for not comfortable at all, and 5 for highly comfortable).
- Review your colleagues’ ratings.
- Reflect upon your rating in comparison to your colleagues.

Why Progress Monitoring?

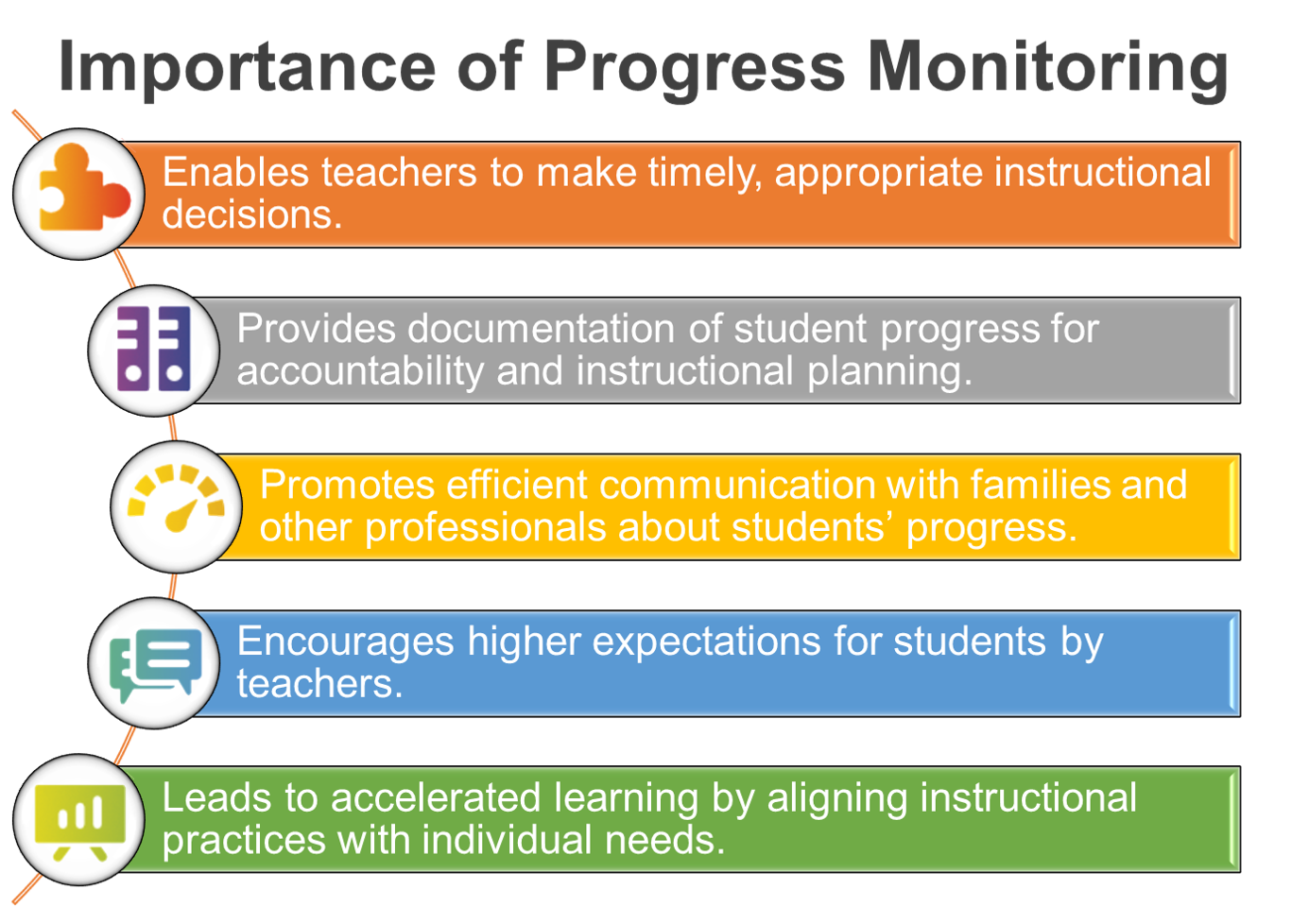
Importance of Progress Monitoring
Regular progress monitoring is an essential component of effective instruction, including specially designed instruction on IEP goals and objectives. Teachers and other service providers need to collect and analyze data on a regular basis to determine how the student is responding to instruction in order to make adjustments. The greater the intensity of the student’s need, the more often data is collected, analyzed, and used to make instructional decisions. Sharing progress data with students and families increases engagement and student’s understanding of their own learning. Frequent progress monitoring is a component of many evidence-based interventions and practices in specially designed instruction, and significant body of research conducted over the past 30 years has shown this method to be useful for a wide range of instructional decisions (Deno, 2003; Fuchs, Deno, & Mirkin, 1984; Good & Jefferson, 1998).
Key Characteristics of Progress Monitoring Tools

Six Major Steps in Effective Progress Monitoring
Select each of the following steps for more information:
Things to Remember
- Good data IN… good data OUT
- Know where your data came from and the validity of the data
- ALL instructional and curriculum decisions should be based on DATA
- Keep it Simple and Efficient!

